Welcome!
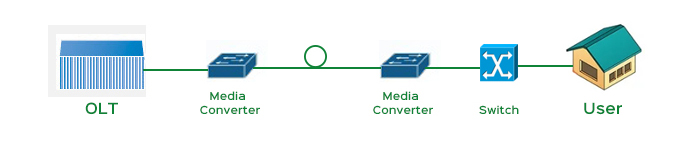
Ethernet+Media Converter (MC) is a transitional point-to-point FTTx scheme that uses the MC method to convert electrical signals into optical signals for long-distance transmission. The point-to-point method has advantages such as ensuring bandwidth speed, high utilization of device ports, good user information security, long transmission distance, and large service area. But at the same time, a large number of optical fibers and optical transceivers need to be laid, resulting in high equipment costs.
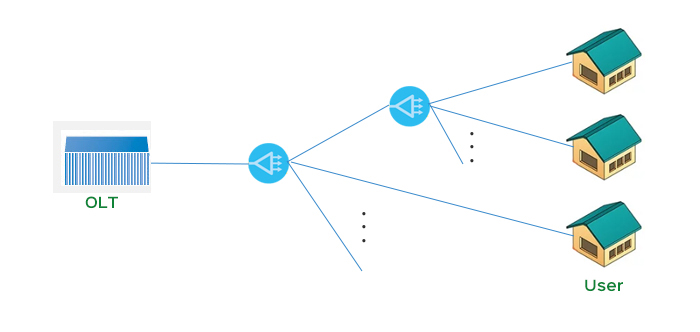
Passive Optical Network (PON) technology is a point to multipoint fiber optic access technology, which consists of an OLT at the central office, an ONU at the user end, and an ODN. The OLT is placed in the central computer room, and the ONT/ONU is placed at the user end. ODN is composed entirely of passive components such as optical splitters, without any active electronic devices or electronic power supplies, and is called PON network. Its architecture mainly involves broadcasting optical signals from a fiber optic line terminal equipment (OLT) downstream through a passive component - an optical splitter - to various optical user terminal equipment (ONT). At present, passive technology is composed of multiple technologies, including APON, GPON, and EPON is also one of the important technologies. The currently widely used PON technology in existing networks includes two mainstream technologies: EPON and GPON.